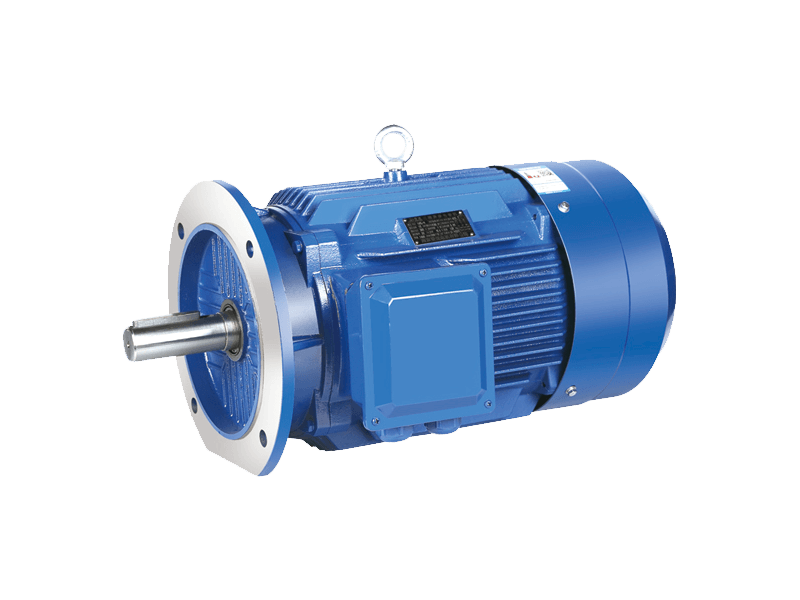
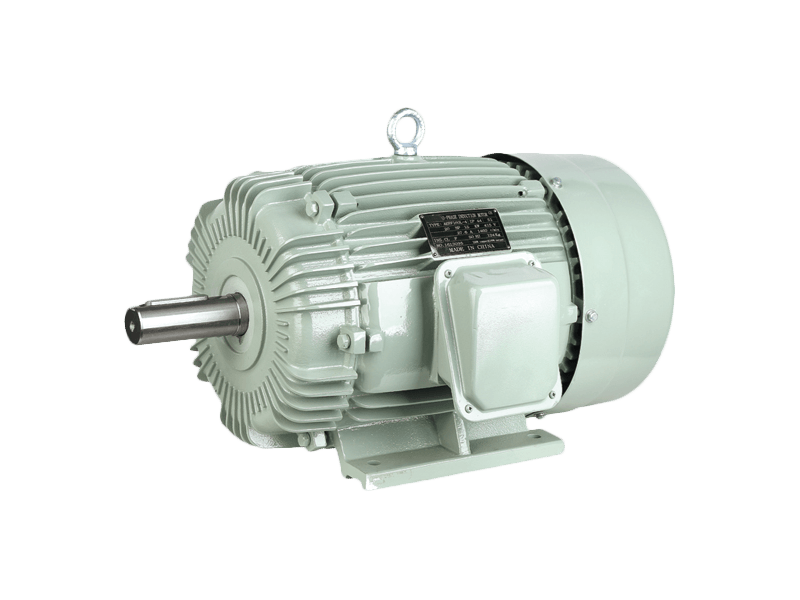
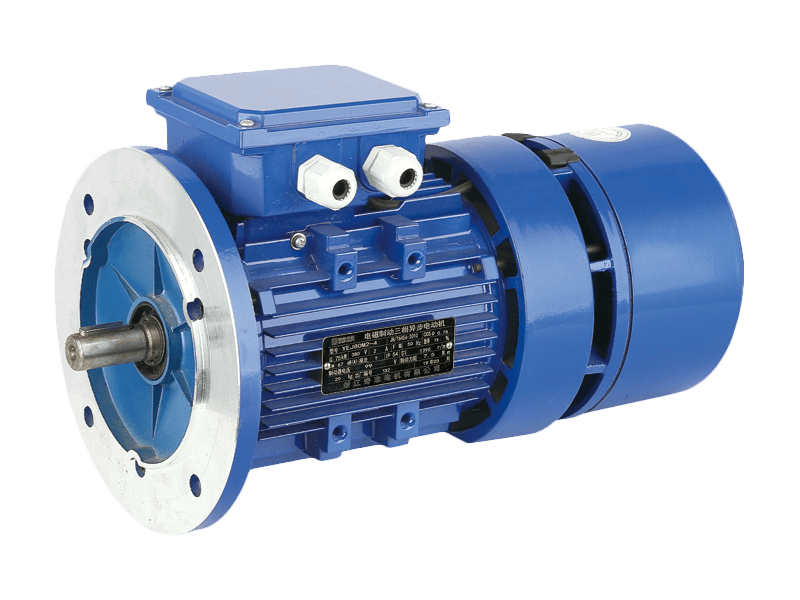
The global market for the electric motor, a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, is undergoing a period of significant expansion and technological refinement. As a foundational component in an immense range of products and systems, the electric motor is at the heart of industrial automation, consumer appliances, personal mobility, and emerging green technologies. The ongoing developments surrounding the electric motor are driven by demands for higher efficiency, greater power density, improved control, and broader integration into electrified systems.
At its core, the function of an electric motor relies on electromagnetic principles to generate rotational force. This fundamental technology has been refined over decades, resulting in various types of electric motor designs, including alternating current (AC) induction motors, brushed and brushless direct current (DC) motors, and synchronous motors. Each type of electric motor offers distinct performance characteristics, making it suitable for specific applications. The continuous improvement in materials, such as better magnetic alloys and high-grade copper windings, enhances the efficiency and durability of the modern electric motor.
Industrial applications continue to represent a major segment of electric motor demand. In manufacturing, the electric motor drives conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, fans, and machine tools. The reliability and controllability of an industrial electric motor are critical for maintaining production uptime and efficiency. The integration of the electric motor with advanced variable frequency drives allows for precise speed and torque control, pilot to substantial energy savings in applications with variable loads. This focus on efficiency is a key trend, pushing the development of premium efficiency classes for the industrial electric motor.
Perhaps the many visible growth driver for electric motor technology is its central role in the transition to electric mobility. In electric vehicles, the traction electric motor is a primary component, determining factors like acceleration, range, and overall vehicle performance. Advances in permanent magnet materials and power electronics have led to electric motor designs that are more compact, powerful, and efficient than previous generations. This application pushes the boundaries of electric motor technology, requiring solutions that manage heat, reduce weight, and deliver power reliably under diverse operating conditions.
Beyond mobility, the electric motor is enabling a wider shift toward electrification in various sectors. In residential and commercial buildings, high-efficiency electric motors are found in HVAC systems, refrigerators, and appliances. The trend toward electrification in areas like heating is also increasing the use of specific types of electric motor-driven compressors in heat pumps. Furthermore, the proliferation of automated and robotic systems across logistics, healthcare, and services relies heavily on compact, precise, and reliable electric motor actuators.
The innovation trajectory for the electric motor is set to continue. Key areas of development include further improvements in efficiency to meet stringent global energy regulations, the use of new materials to reduce reliance on uncommon-earth elements, and the deeper integration of smart sensors and connectivity for condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. The electric motor is also a critical enabler for renewable energy systems, powering the generators in wind turbines and the tracking systems in solar installations. As the world increasingly turns to electricity as a primary energy carrier, the humble yet sophisticated electric motor will remain an indispensable and evolving technology, quietly powering progress across virtually every facet of modern life and industry. Its ongoing evolution is not merely about incremental improvement but about enabling a more automated, efficient, and electrified future.