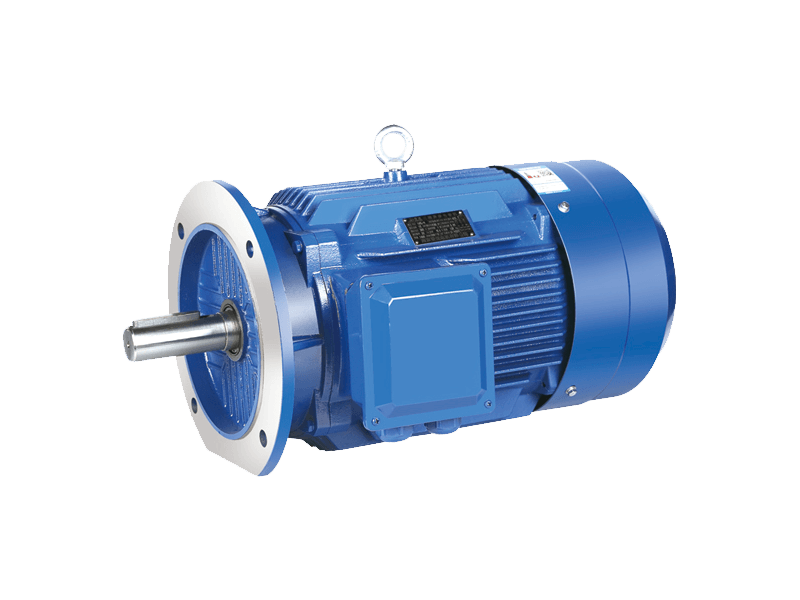
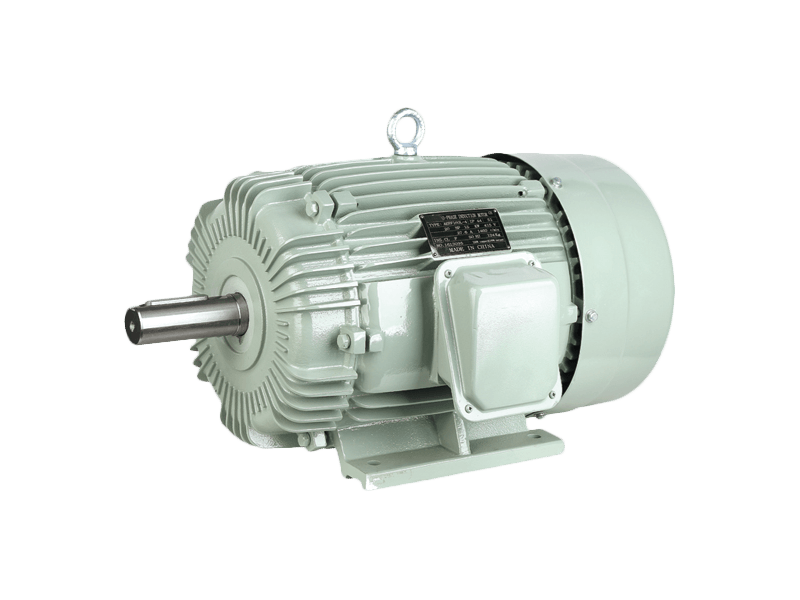
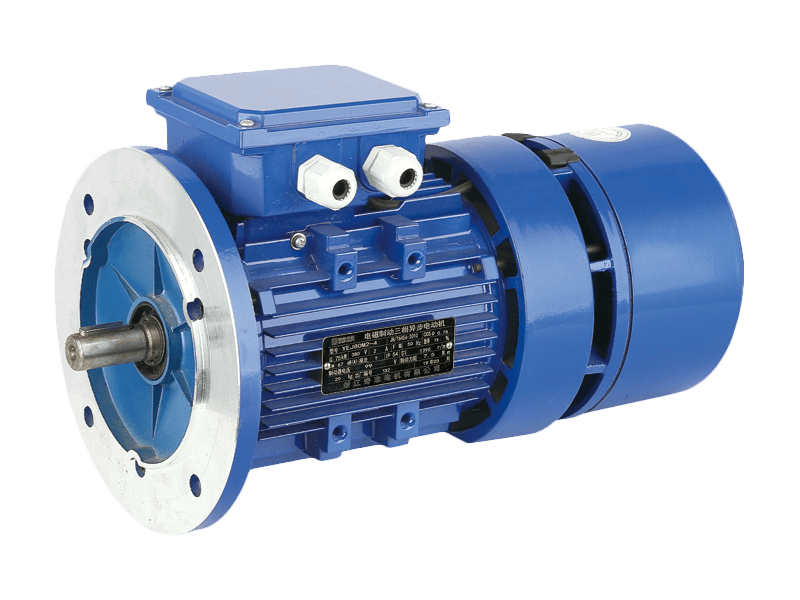
The alternating current (AC) motor continues to serve as a fundamental and indispensable component within the global industrial landscape and a vast array of everyday appliances. Despite the growing prominence of alternative drive technologies in specific applications, the AC motor remains the dominant choice for numerous applications due to its proven reliability, straightforward construction, and cost-effective operation. The enduring presence of the AC motor underscores its critical function in powering systems that form the backbone of modern infrastructure, manufacturing, and commercial operations.
At its core, the operational principle of the AC motor is both elegant and robust. It converts alternating current electrical energy into rotational mechanical energy through the interaction of a rotating magnetic field generated in the stator and currents induced in the rotor. This design, with few moving parts and no requirement for physical electrical contacts to the rotor in common induction types, contributes to the notable durability and low maintenance needs of a standard AC motor. These characteristics ensure that an AC motor can provide years of continuous service in demanding environments, from factory floors to HVAC systems.
The application spectrum for the AC motor is exceptionally broad. In industrial settings, the AC motor is the primary driver for machinery including pumps, compressors, fans, conveyor belts, and machine tools. Its ability to deliver constant speed under variable load conditions makes the AC motor highly suitable for these continuous-process applications. Beyond heavy industry, the AC motor is ubiquitous in commercial and residential contexts. It operates within household appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, as well as in commercial equipment such as elevators, escalators, and ventilation systems. This pervasive use highlights the adaptability and scalability of AC motor technology across different power and size requirements.
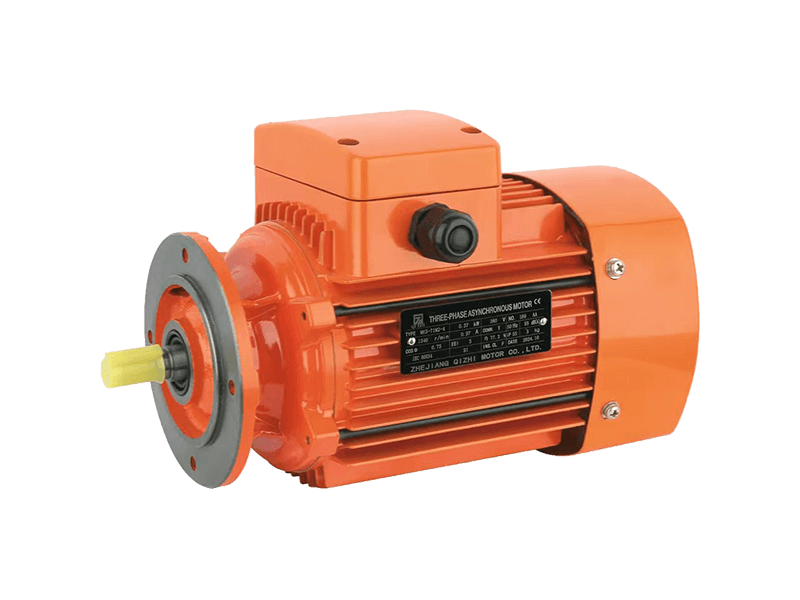
Technological evolution has not left the traditional AC motor behind. The integration of the AC motor with variable frequency drive (VFD) technology represents a significant advancement. A VFD allows for precise control over the speed and torque of an AC motor by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to it. This pairing transforms the fixed-speed AC motor into a highly efficient, controllable asset. Using a VFD with an AC motor can cause substantial energy savings, particularly in applications like pumping or fan systems where demand fluctuates, reducing overall operational costs and environmental impact.
Ongoing material science and engineering refinements continue to improve the performance profile of the AC motor. Developments in high-efficiency designs, often classified under international efficiency standards, focus on reducing electrical losses within the copper windings and the magnetic steel core of the AC motor. These improvements enhance the overall energy conversion efficiency of the AC motor, pilot to lower electricity consumption over its operational lifetime. Additionally, advancements in insulation materials and bearing technologies contribute to extending the service life and reliability of the modern AC motor.
The AC motor is expected to maintain its central position in global electromechanical systems. Its future is likely characterized by continued incremental improvements in efficiency, integration with digital control and monitoring systems for predictive maintenance, and adaptation within hybrid systems. While new motor technologies may capture attention for niche applications requiring exceptional control or power density, the simplicity, ruggedness, and economic advantage of the AC motor secure its ongoing relevance.