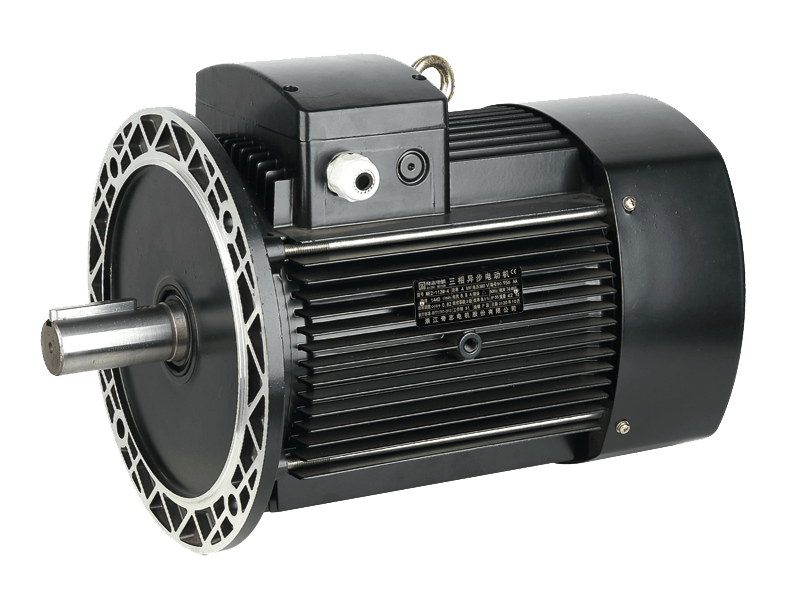
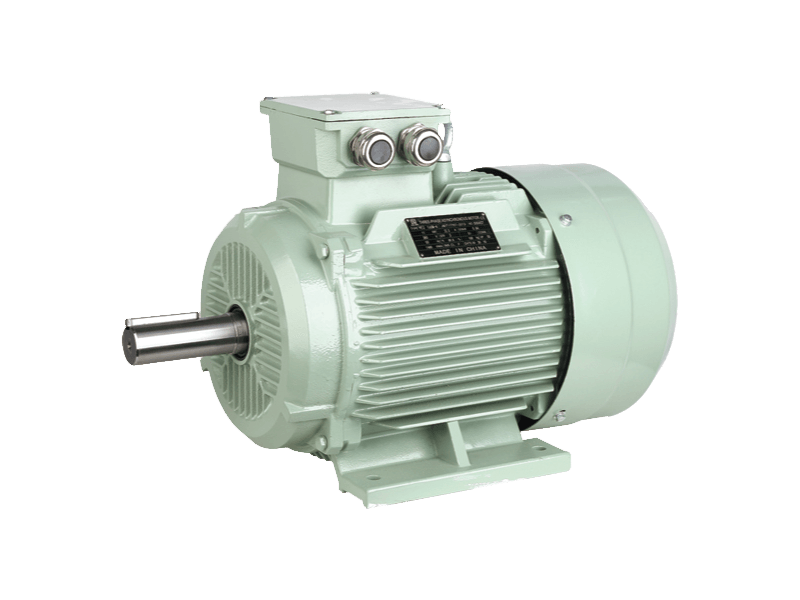
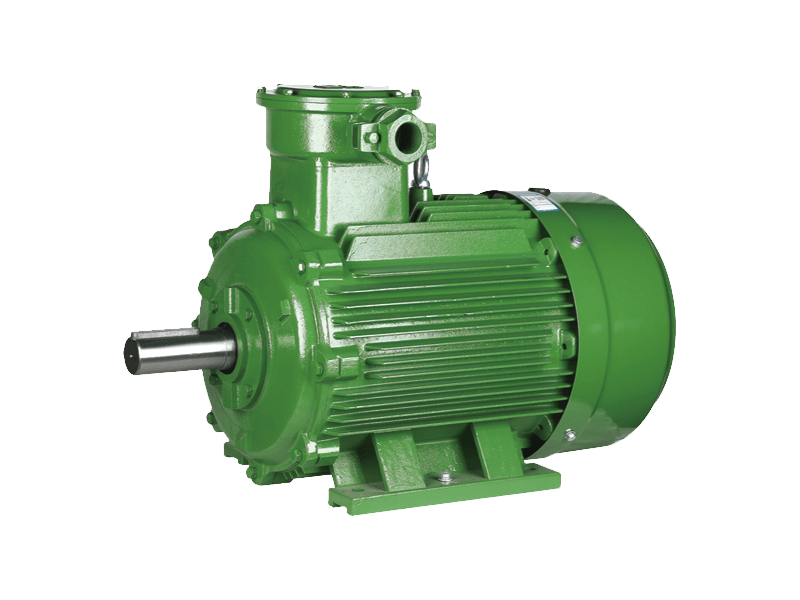
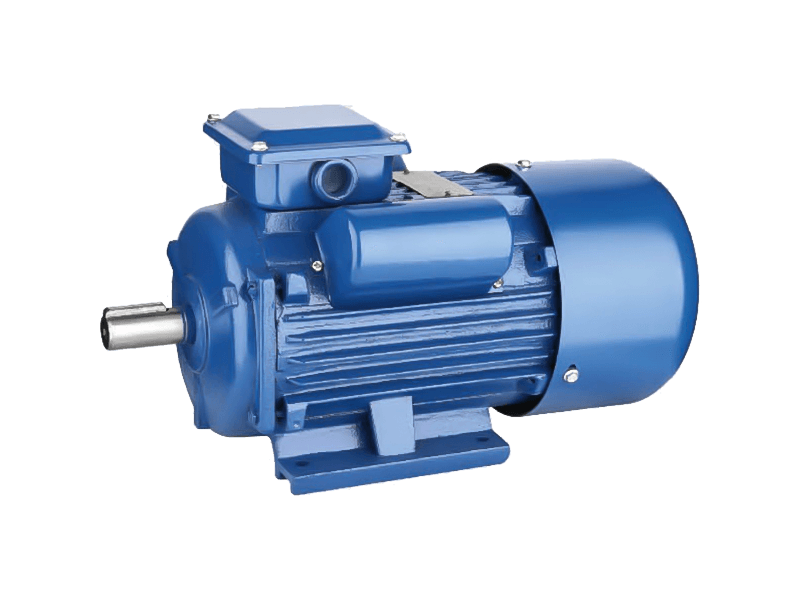
A fundamental component underpinning modern industry and commercial operations continues to be the three phase motor. This type of electric motor, designed to operate on a three-phase alternating current (AC) power supply, is prized for its efficiency, reliability, and self-starting capability. The widespread application of the three phase motor across sectors such as manufacturing, HVAC, water treatment, and material handling underscores its irreplaceable role in driving compressors, pumps, fans, conveyors, and a vast array of other machinery.
The operational advantage of the three phase motor lies in its elegant and robust design. Unlike single-phase motors, the three phase motor does not require a starting capacitor or switch mechanism to initiate rotation. When connected to a three-phase power source, the motor's stator windings produce a rotating magnetic field. This rotating field induces a current in the rotor, causing it to turn smoothly and with high starting torque. This inherent simplicity and power make the three phase motor exceptionally reliable and efficient, especially in demanding continuous-duty applications. The balanced load it presents to the electrical grid is another significant benefit of the three phase motor.
In industrial settings, the three phase motor is the prime mover for critical systems. It drives the hydraulic pumps in injection molding machines, powers the large fans in industrial ventilation systems, and turns the massive drums in mixers and mills. The durability and consistent power output of a three phase motor make it suitable for environments where equipment must run for extended periods, often under significant load. The ability of a three phase motor to handle high starting torque is crucial for applications like conveyor belts starting under load or crushers beginning to process material.
The design evolution of the three phase motor focuses relentlessly on improving energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. Modern iterations, often compliant with international efficiency classification standards, utilize higher-grade electrical steel, optimized winding designs, and improved cooling systems. These enhancements reduce electrical losses, meaning a contemporary three phase motor converts a greater percentage of incoming electrical energy into useful mechanical work. This focus on efficiency is a direct response to global priorities on energy conservation and reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations. Furthermore, the three phase motor is increasingly paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs), which allow for precise control of motor speed. This not only saves energy by matching motor output to actual demand but also reduces mechanical stress on both the three phase motor and the driven equipment.
The three phase motor will continue to be a cornerstone of industrial and commercial power transmission. Future developments are likely to involve further incremental gains in material science for even greater efficiency, as well as deeper integration with digital control systems for smart grid compatibility. The rise of industrial IoT will see more three phase motors equipped with connectivity for real-time performance monitoring and optimization. While new motor technologies emerge, the proven reliability, efficiency, and versatility of the three phase motor ensure its enduring presence as the workhorse of global industry, quietly powering the essential processes that support the economy and daily life.