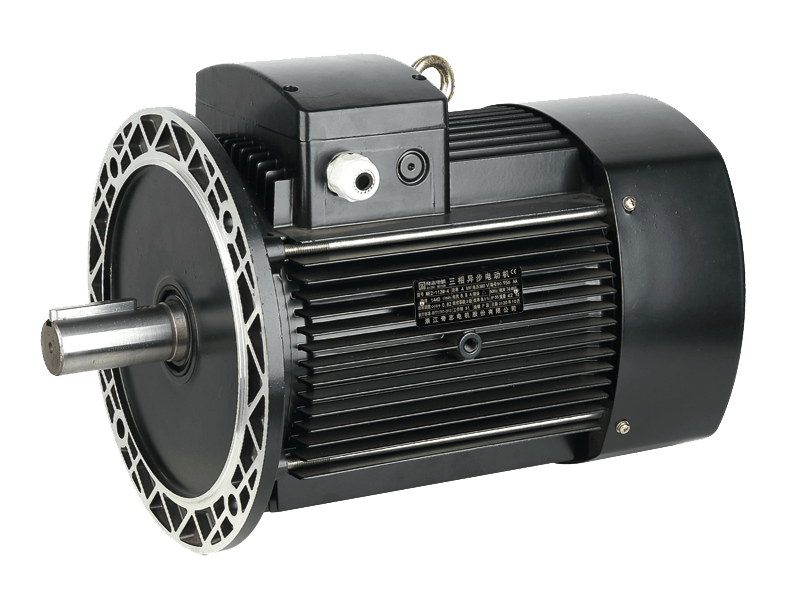
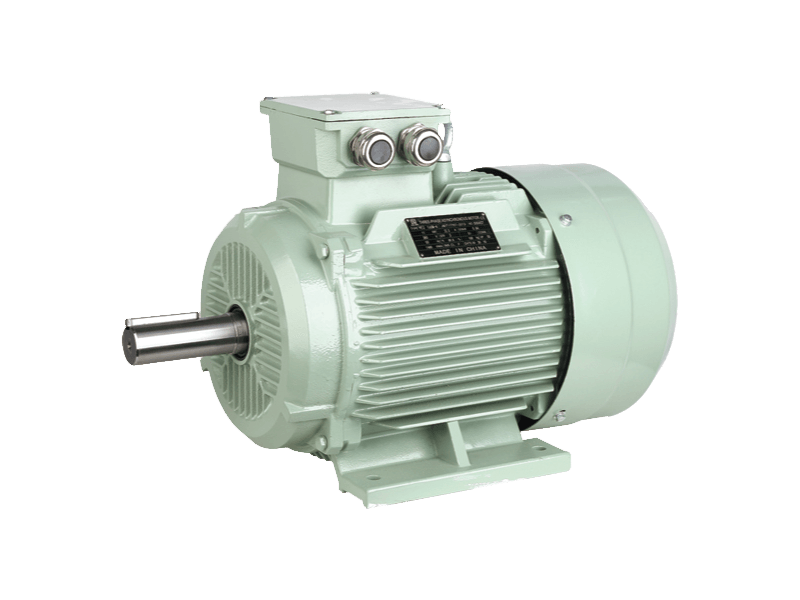
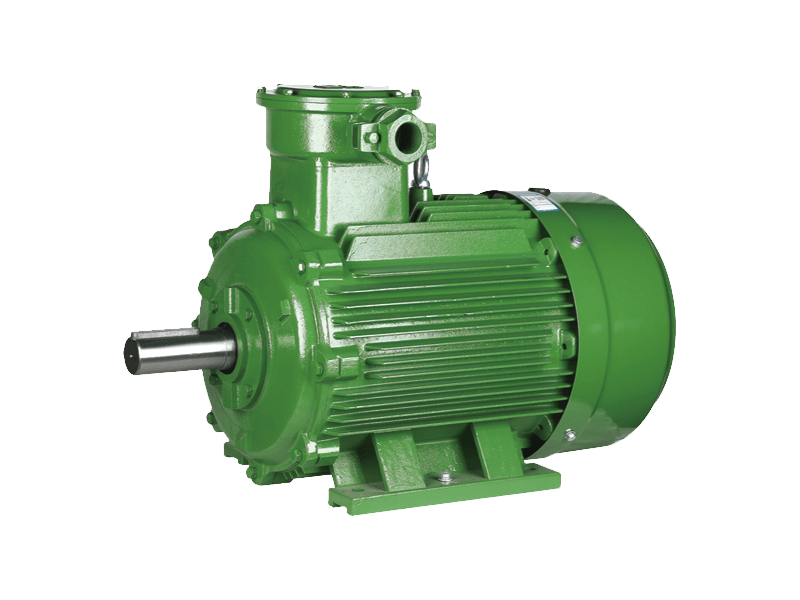
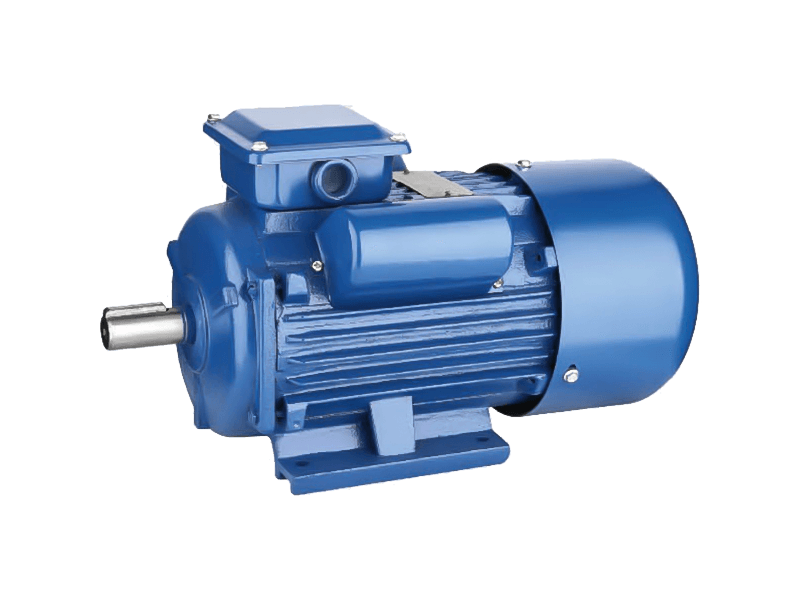
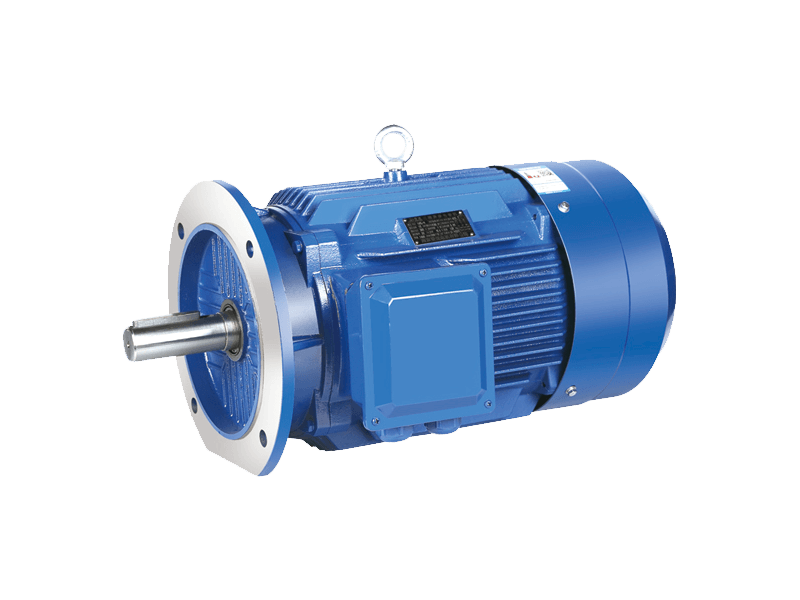
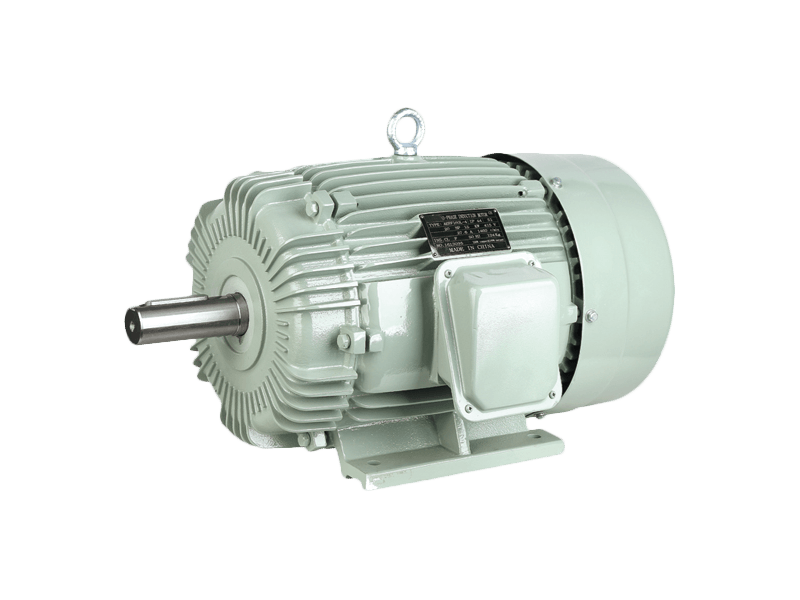
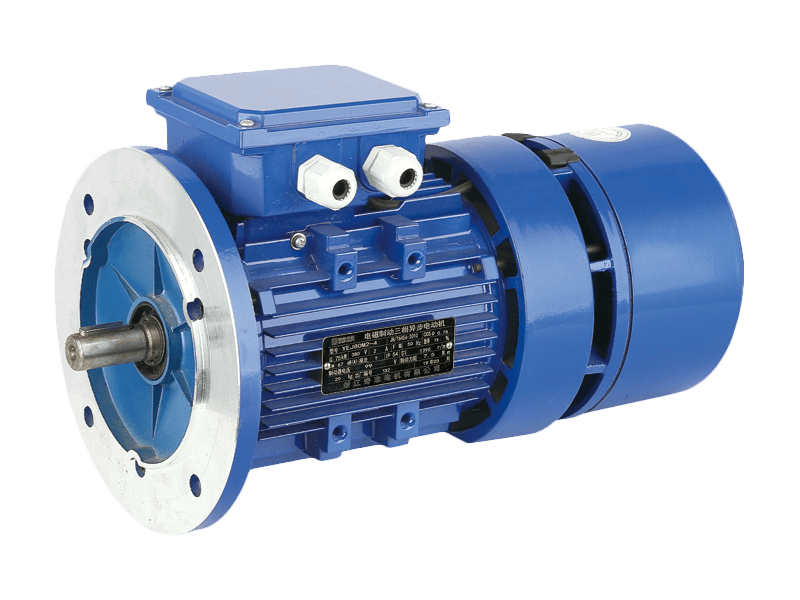
Speed three-phase asynchronous motors are one of the widely used types of electric motors in industrial applications due to their efficiency, robustness, and relatively simple construction. These motors, often referred to as induction motors, operate on alternating current (AC) and are designed to provide reliable power across a variety of industrial settings, from manufacturing plants to commercial and residential systems. Over the years, their applications have expanded, with significant advancements in motor design and technology enhancing their performance and versatility.
In this article, we will explore the impact and evolution of speed three-phase asynchronous motors in industrial settings, highlighting their widespread uses, advantages, and the ongoing innovations driving their performance improvements.
The Mechanics Behind Speed Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
A speed three-phase asynchronous motor works by generating a rotating magnetic field that induces a current in the rotor. This induced current produces torque, causing the rotor to rotate and ultimately powering mechanical equipment. The term "asynchronous" refers to the fact that the speed of the rotor never exactly matches the speed of the rotating magnetic field—hence the term "slip," which is the difference between these two speeds.
These motors are characterized by their simple design and ability to operate at high efficiency, particularly in industrial applications that require constant-speed operations. Unlike synchronous motors, speed three-phase asynchronous motors do not require a constant external power supply to maintain speed, making them suitable for a wide range of dynamic loads.
Efficiency and Energy Saving: A Key Advantage
One of the significant advantages of speed three-phase asynchronous motors is their energy efficiency. These motors are inherently designed to minimize energy loss, especially when compared to other types of electric motors. By utilizing a three-phase system, the motor is able to provide a constant and balanced power supply, ensuring stable and smooth operation.
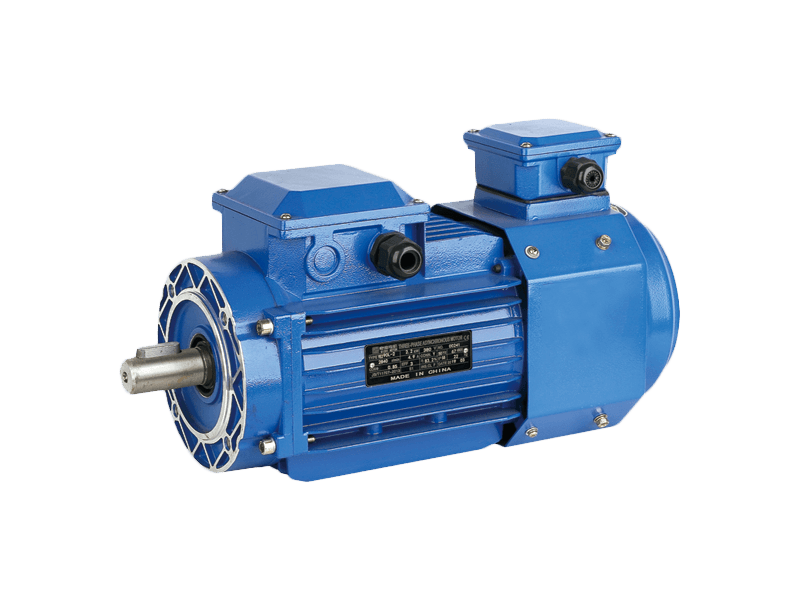
With growing environmental concerns and rising energy costs, businesses are increasingly turning to speed three-phase asynchronous motors as a way to reduce energy consumption and improve the overall efficiency of their operations. For industries such as manufacturing, pumping, and ventilation, where motors are in continuous use, switching to high-efficiency motors can result in substantial cost savings and a lower carbon footprint.
Applications Across Various Industries
Speed three-phase asynchronous motors are used in a wide array of industries, ranging from manufacturing and construction to agriculture and utilities. These motors are typically found in industrial machines like conveyor belts, pumps, fans, compressors, and HVAC systems.
In the manufacturing industry, speed three-phase asynchronous motors drive a variety of machinery, including lathes, milling machines, and assembly lines. Their ability to maintain a constant speed and handle heavy loads makes them indispensable in environments where reliability and continuous operation are critical. These motors are also used in industrial pumps for fluid handling, where their robust performance ensures smooth water, oil, or gas flow.
In the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) industry, speed three-phase asynchronous motors power ventilation systems, air conditioners, and fans, helping to regulate air circulation and maintain temperatures. The energy efficiency of these motors is particularly valuable in large-scale commercial and residential buildings, where HVAC systems consume a significant portion of energy.
The Role of Smart Technologies in Speed Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
While speed three-phase asynchronous motors have long been recognized for their reliability and efficiency, the integration of smart technologies has elevated their performance to new levels. The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and automation has enabled industries to monitor and control their motors remotely, optimizing performance and maintenance.
Advanced sensors and motor control systems allow operators to collect real-time data on motor performance, including factors such as temperature, vibration, and energy consumption. This data can be analyzed to predict potential failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime. Moreover, variable frequency drives (VFDs) have become common in conjunction with these motors, allowing for adjustable motor speed, which improves energy efficiency and operational flexibility.