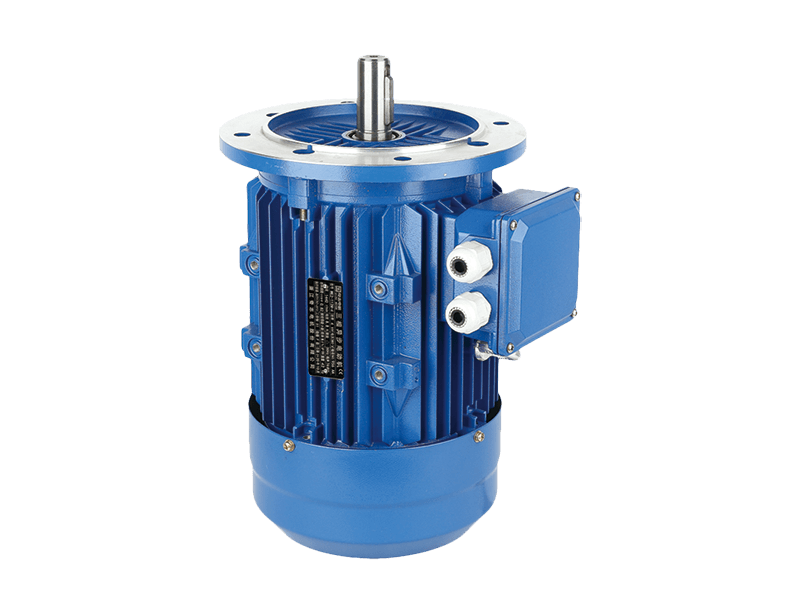
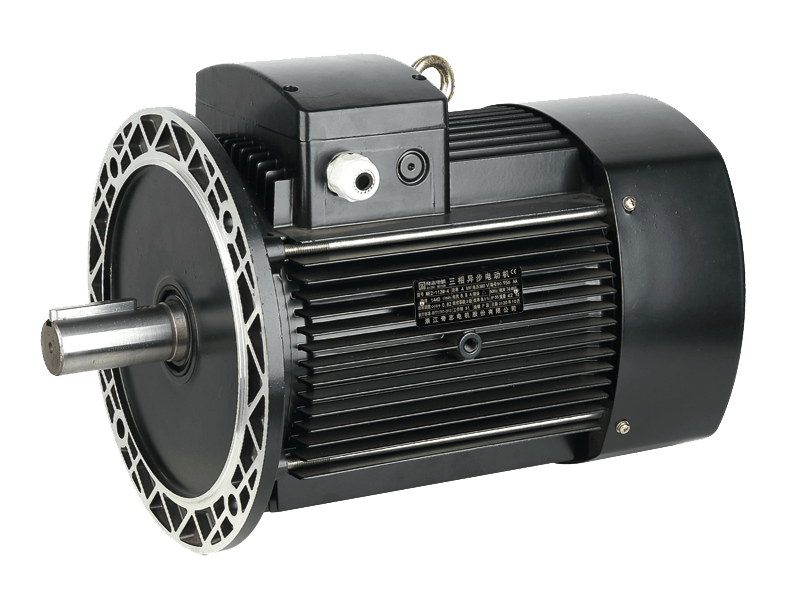
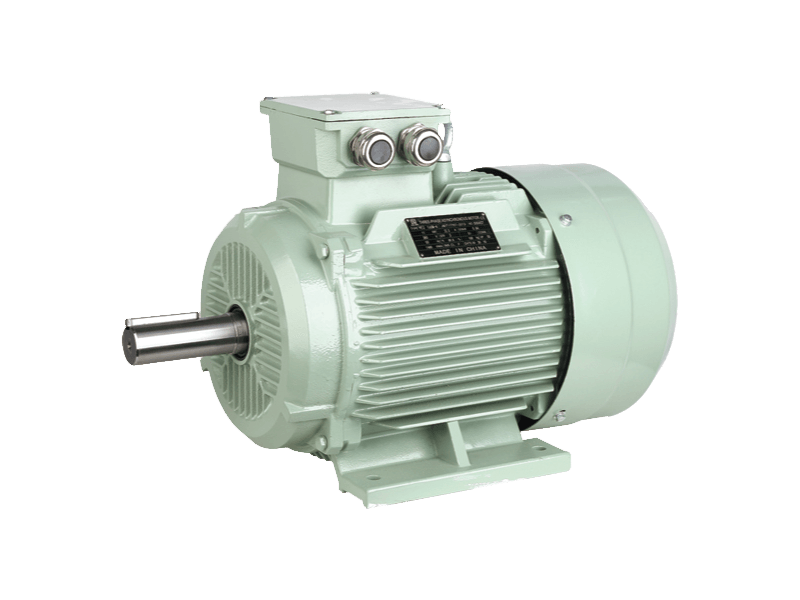
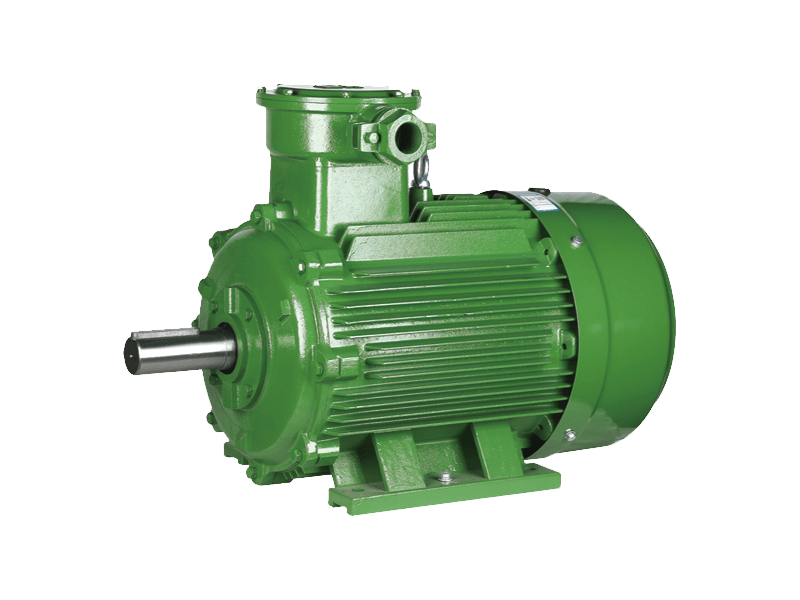
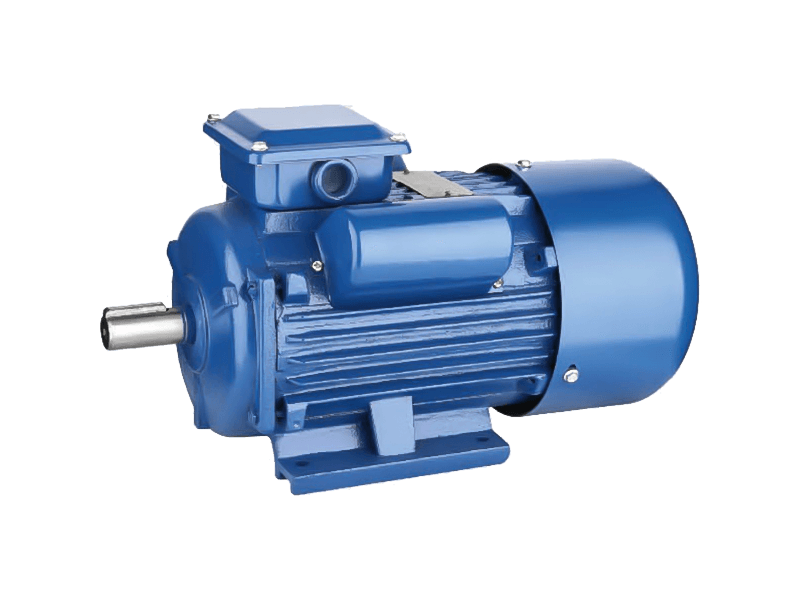
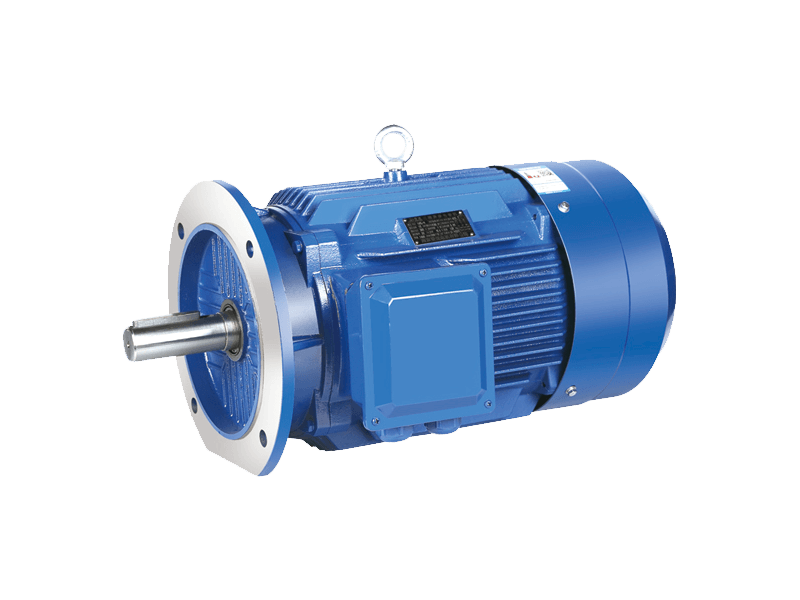
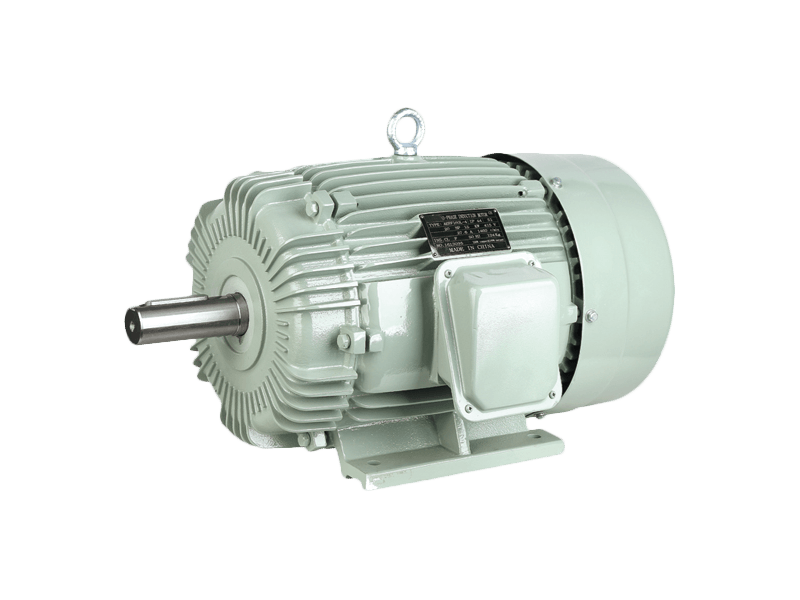
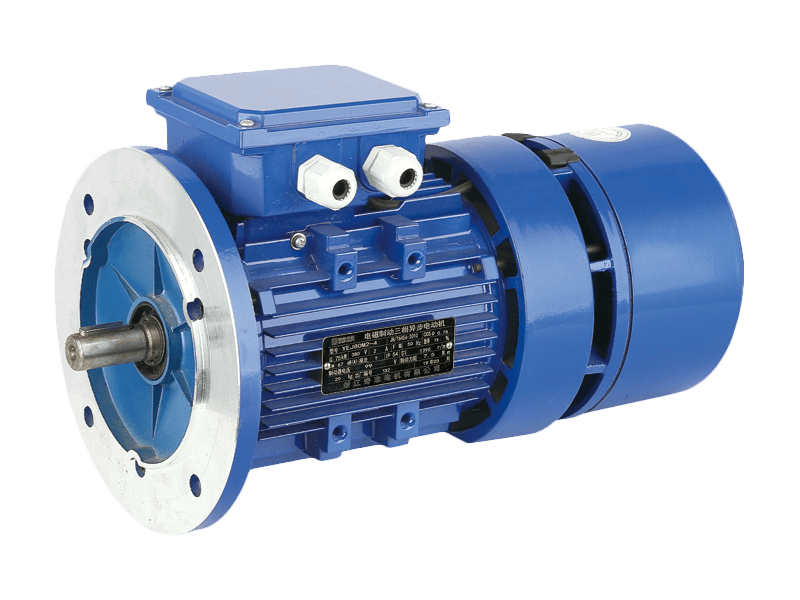
Three phase motor is a type of electric motor that operates with three electrical phases. It is commonly used for industrial and commercial applications, such as pumps, fans, compressors, mixers, agitators, mills, conveyors, and cranes.
How a three phase motor works
A three phase motor consists of a stator that is internally wired in a delta configuration with windings for each phase. Each winding energizes a field pole in the stator. The field poles change periodically as a result of the current being applied, and the changing field poles generate an alternating magnetic field around the rotor that rotates within the ac case.
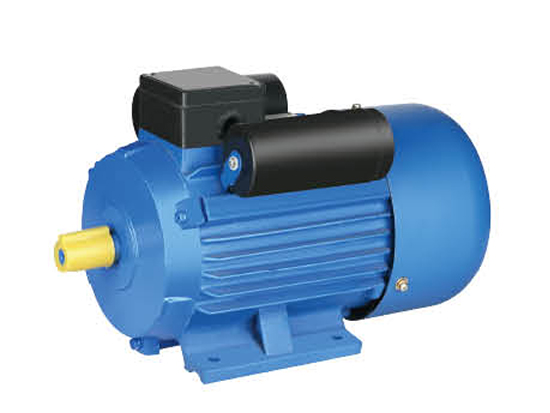

The rotor is made of an aluminum or copper laminated core that has parallel slots in its interior. These are fitted with heavy copper or aluminum bars that are short-circuited by end rings for mechanical support and to add external resistance to the circuitry.
When a motor is connected to an AC supply, the magnetic field that is generated in the stator induces a current in the rotor which in turn produces a torque at the shaft of the motor. This torque is dependent on the speed of the rotor relative to the stator's rotating magnetic field, and this difference is referred to as slip.
How to Check a Three-Phase Motor
The easiest way to determine whether a three-phase motor is connected to a power supply is to connect it to a multimeter and measure the voltage. A single-phase motor should give a reading of 230 volts, while a three-phase motor should give a reading of about 208 volts.