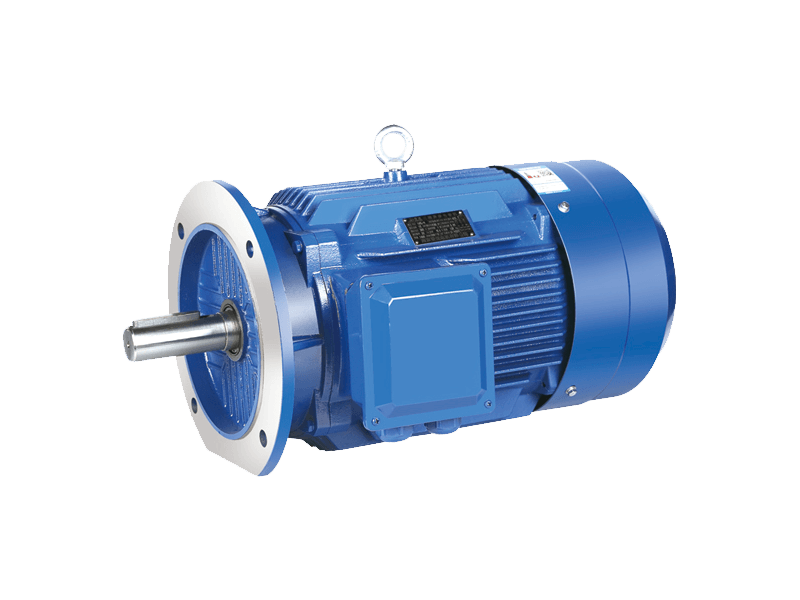
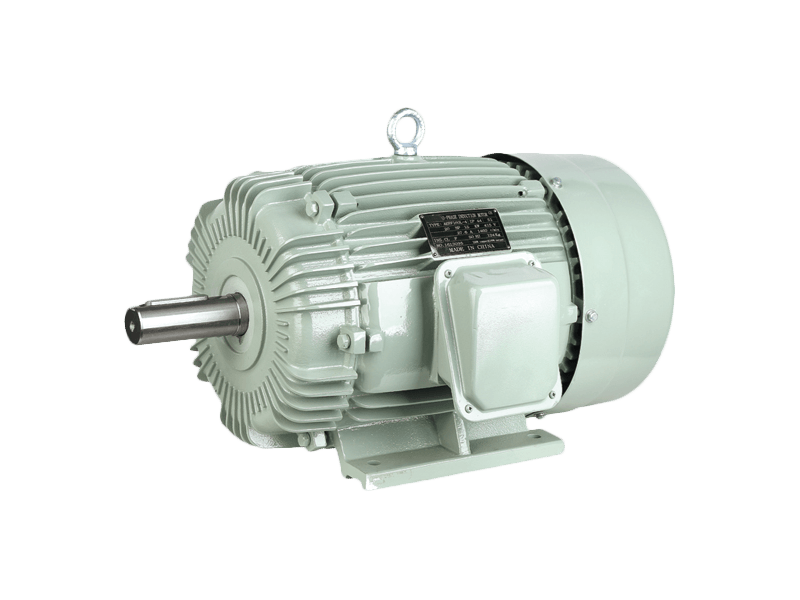
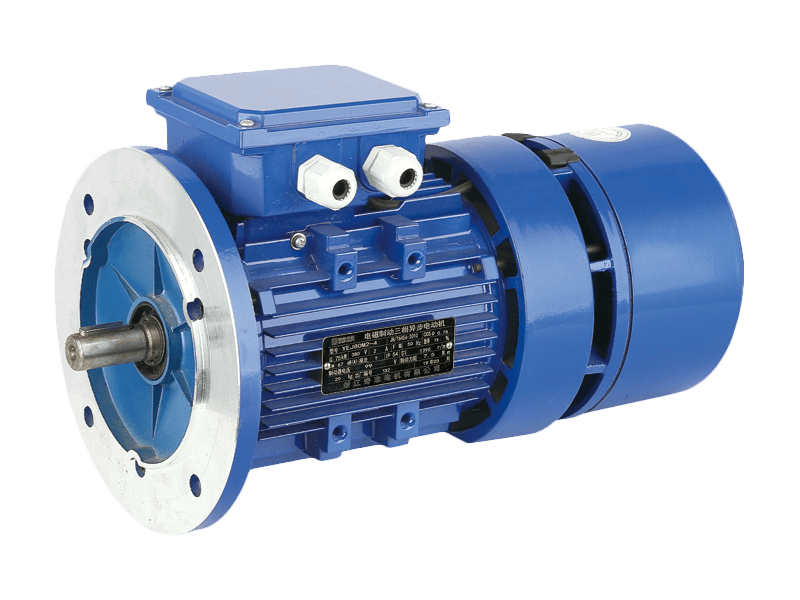
The journey toward global electrification and automation relies heavily on a technological cornerstone that has been refined for over a century: the AC motor. Operating on alternating current, the AC motor is an indispensable component in a vast array of applications, from industrial machinery and home appliances to commercial HVAC systems and transportation. The enduring prevalence and ongoing evolution of the AC motor demonstrate its unparalleled combination of reliability, efficiency, and versatility in converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation.
At its core, the functionality of an AC motor is based on electromagnetic induction. When alternating current is supplied to the motor's stator windings, it creates a rotating magnetic field. This field interacts with the rotor, inducing currents that generate a force, causing the rotor to turn. This elegant principle allows the AC motor to operate without the brushes and commutators found in many DC motors, pilot to reduced maintenance, longer service life, and robust performance in demanding environments. The widespread availability of AC power from electrical grids makes the AC motor a natural and convenient choice for stationary applications.
The application spectrum for the AC motor is remarkably broad. In the industrial sector, the AC motor is the driving force behind pumps, compressors, fans, conveyors, and machine tools. Its ability to provide consistent torque and operate continuously under load makes it the workhorse of factories and processing plants. In the commercial and residential realms, the AC motor is embedded within refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioning units, and ventilation fans. The scalability of AC motor design, from fractional horsepower units in small appliances to multi-megawatt versions in heavy industry, underscores its fundamental adaptability.
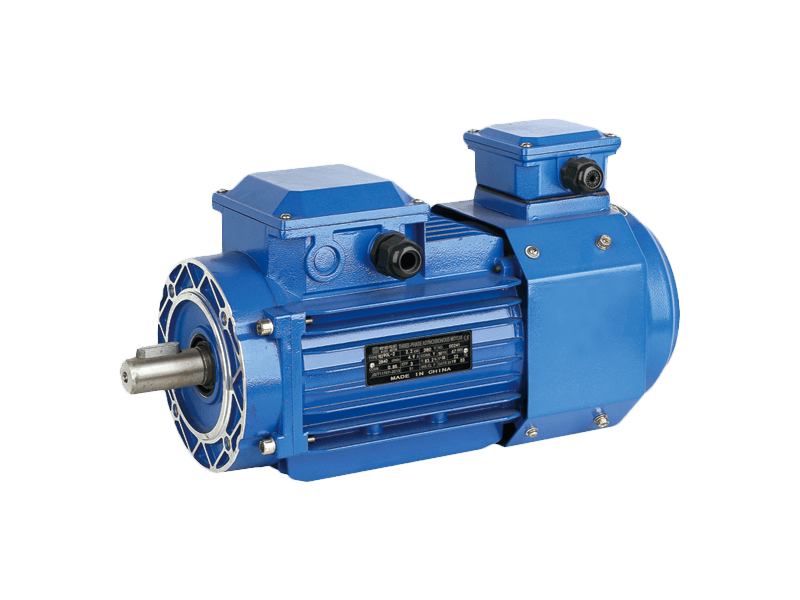
Technological progress continues to enhance the performance and application of the AC motor. A significant development is the integration of variable frequency drives (VFDs). By controlling the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, a VFD allows for precise adjustment of an AC motor's speed and torque. This capability translates into substantial energy savings, as the motor can operate at ideal speeds for the task rather than running at a constant rate. It also reduces mechanical stress during startup and enables finer process control. Furthermore, advances in materials, such as improved electrical steels and high-grade copper windings, have steadily increased the efficiency of the modern AC motor, aligning with global energy conservation goals.
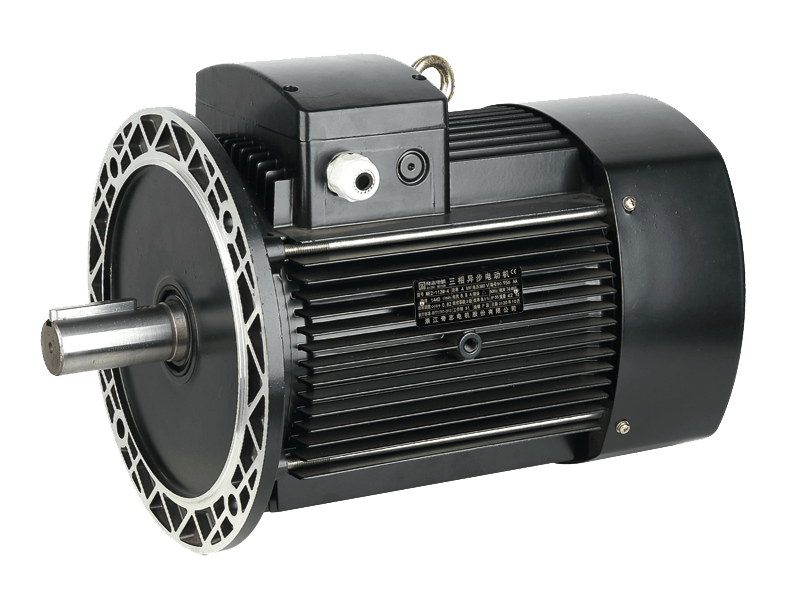
The design and selection of an AC motor are guided by specific operational requirements. Key considerations include power rating, speed, torque characteristics, and the duty cycle (whether it runs continuously or intermittently). Engineers choose between various types, such as the rugged and simple induction motor or the highly synchronous motor, based on the needs for precision speed control or starting torque. The robust construction of a typical industrial AC motor, featuring sealed bearings and protective enclosures, ensures reliable operation even in the presence of dust, moisture, or temperature variations.
The AC motor is poised to remain central to electrification trends while adapting to new demands. Its role is critical in emerging sectors like renewable energy, where AC motors are used in positioning systems for solar panels and in auxiliary systems for wind turbines. The ongoing integration of smart sensors and connectivity will give rise to more intelligent AC motors capable of self-diagnosis and communication within networked industrial systems, facilitating predictive maintenance.