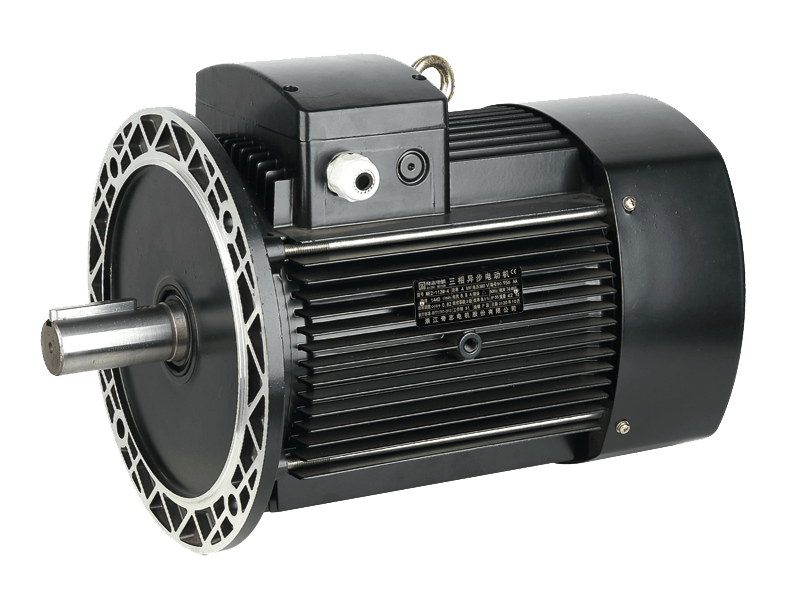
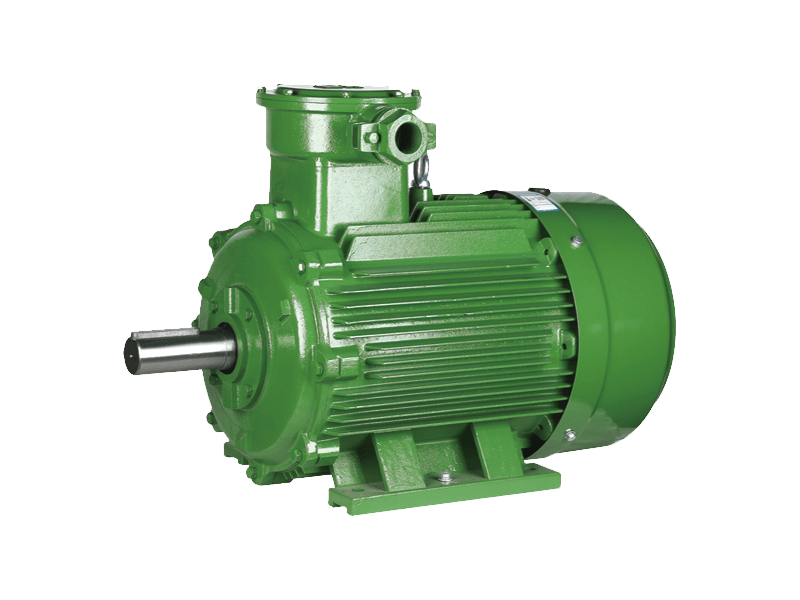
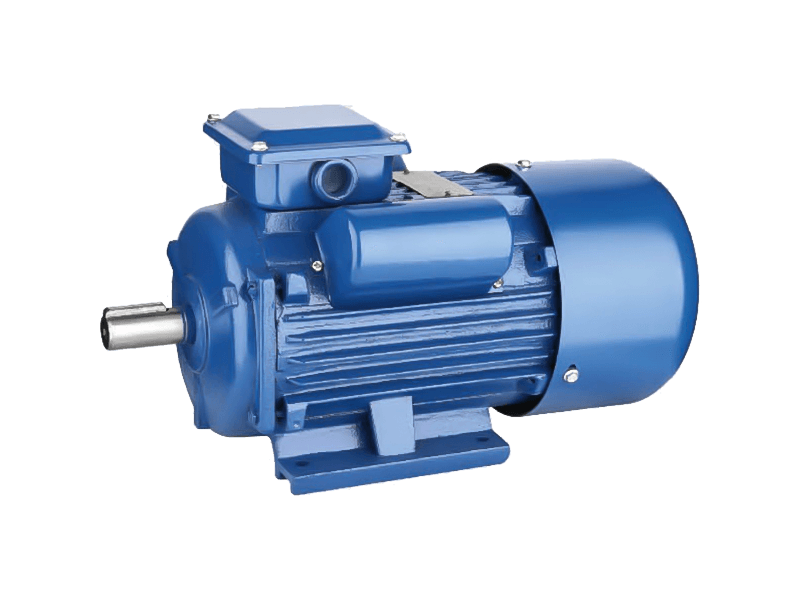
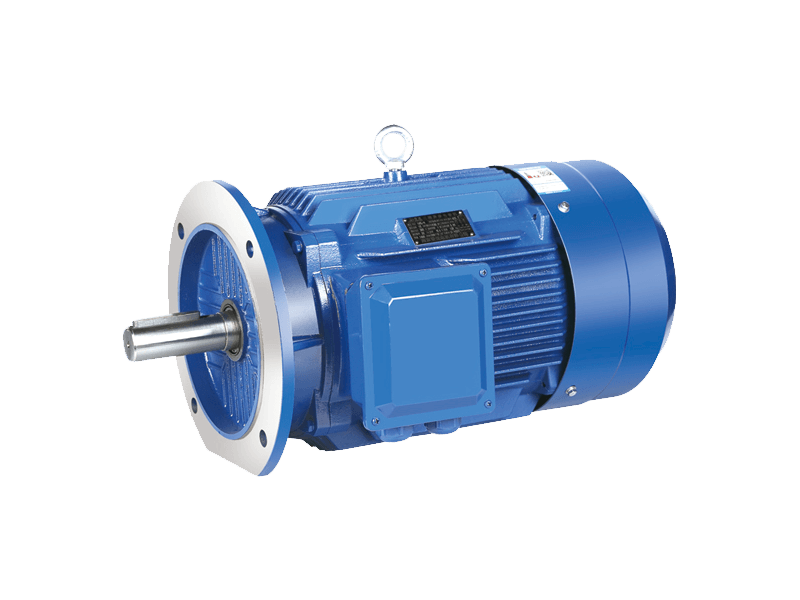
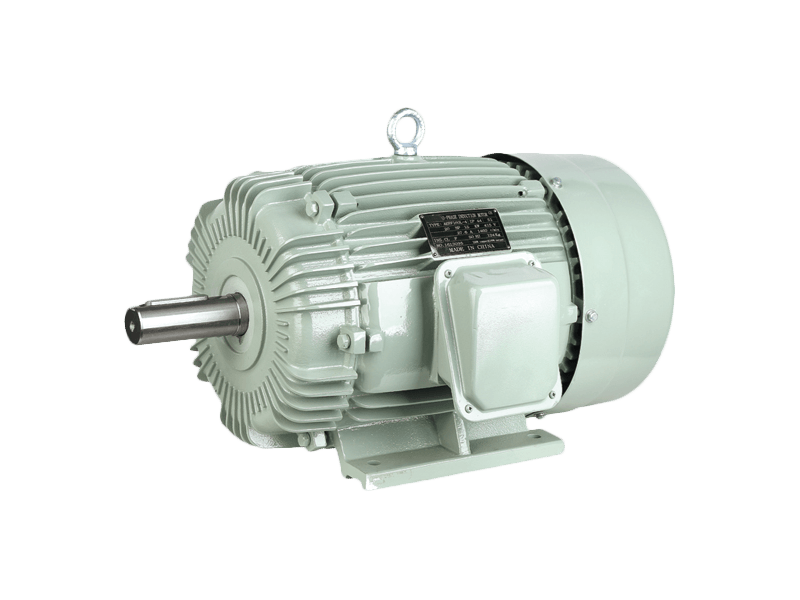
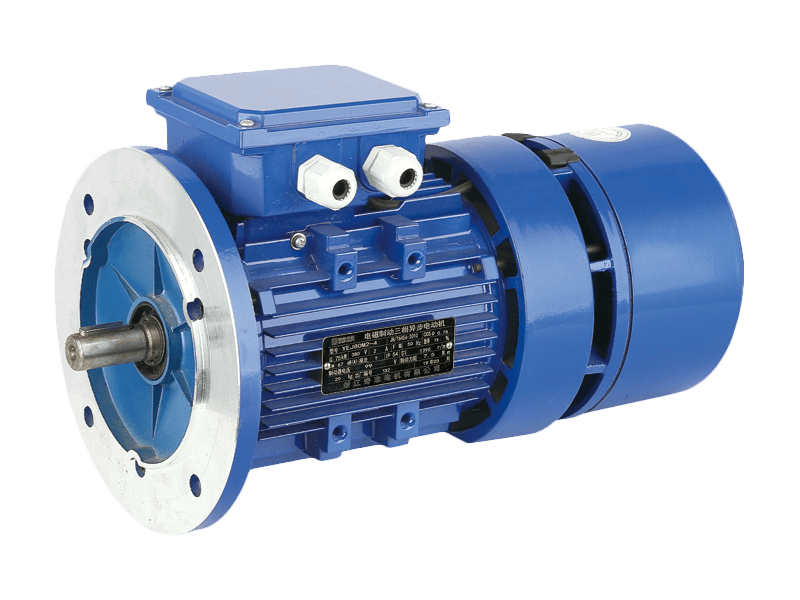
In the realm of industrial motors, performance parameters such as vibration and noise levels have become increasingly critical. Among the wide array of motors used in manufacturing, processing, and mechanical operations, the Y2 motor has distinguished itself as a top choice for applications demanding high reliability combined with quietness and stability. Known for its slight vibration, low noise, and robust design, the Y2 motor is gaining prominence as industries seek to improve operational environments while maintaining efficiency and durability.
Understanding the Y2 Motor and Its Advantages
The Y2 motor is a three-phase asynchronous motor designed to meet stringent industrial standards for performance and environmental friendliness. One of its notable features is the remarkably low vibration it produces during operation. Vibration in electric motors can to premature wear, misalignment of connected equipment, and increased maintenance costs. The Y2 motor’s design addresses these issues head-on by incorporating precise manufacturing tolerances, balanced rotors, and high-quality bearings, ensuring smooth rotation with oscillation.
In addition to vibration control, noise reduction is another hallmark of the Y2 motor. Industrial facilities are often challenged by noise pollution, which affects not only worker comfort and health but also overall workplace safety and regulatory compliance. The Y2 motor’s structure and materials have been optimized to minimize operational noise, making it suitable for environments where quiet performance is essential, such as hospitals, laboratories, and office buildings, as well as conventional factories.
Technical Features Contributing to Low Vibration and Noise
Several key design elements enable the Y2 motor to achieve its low vibration and noise performance:
Precision Balancing: The rotor assembly in the Y2 motor is meticulously balanced during manufacturing to reduce mechanical imbalance. This significantly diminishes vibration that typically results from uneven weight distribution.
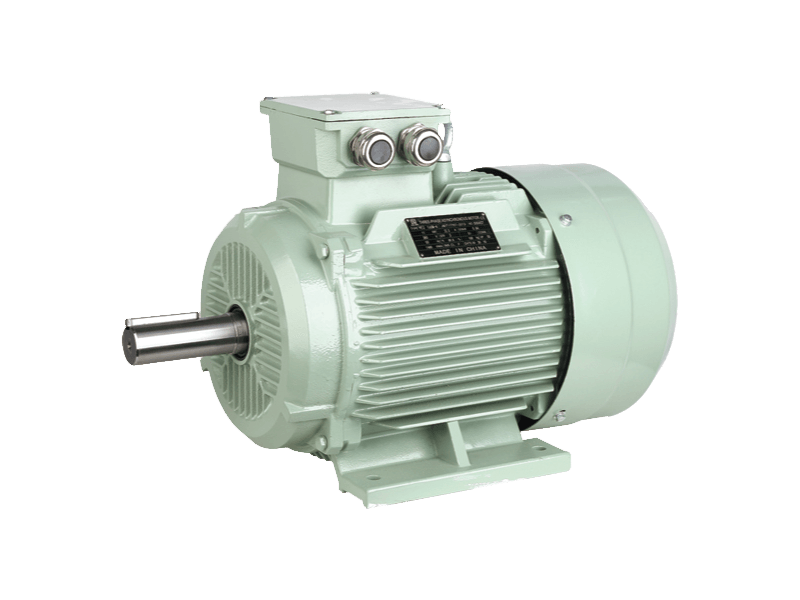
High-Quality Bearings: The use of premium-grade ball or roller bearings reduces friction and mechanical noise. Bearings are carefully selected to withstand operational stresses and maintain smooth shaft rotation.
Robust Frame and Housing: The motor frame is engineered to dampen vibrations. Reinforced cast iron or steel housings help absorb mechanical shocks and reduce noise transmission to the surroundings.
Optimized Winding Techniques: The stator windings are arranged to minimize electromagnetic noise, a common source of hum or buzz in electric motors.
Improved Cooling Systems: Efficient cooling fans and airflow paths help maintain motor temperature without generating excessive noise.
Applications Benefiting from the Y2 Motor’s Stability
Because of its low vibration and noise characteristics, the Y2 motor is well-suited to a wide variety of industrial and commercial applications:
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning units rely on quiet, reliable motors to maintain comfort without disrupting building occupants. The Y2 motor fits perfectly here by delivering smooth, quiet operation.
Pumps and Compressors: In water treatment plants, agricultural irrigation, and chemical processing, pumps driven by Y2 motors experience less mechanical stress and noise, improving longevity and system performance.
Machine Tools and Precision Equipment: Industries requiring high precision, such as electronics manufacturing and metalworking, benefit from the Y2 motor’s vibration control, which prevents detrimental oscillations that could affect machining accuracy.
Conveyors and Material Handling: Reduced vibration translates into smoother movement of goods and less wear on conveyor components, enhancing overall reliability.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Environments where noise must be minimized for safety and comfort, including hospitals and research labs, increasingly adopt Y2 motors.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
The low vibration and noise profile of the Y2 motor not only enhances operational comfort but also contributes to longer motor life and decreased maintenance costs. Vibration is a primary cause of mechanical wear and failure in motor-driven equipment, so it helps avoid costly downtime and repairs.
Additionally, quieter motors support compliance with workplace noise regulations, helping companies avoid fines and improve worker satisfaction and productivity. Lower noise emissions also open doors for industrial facilities to operate in noise-sensitive areas, such as urban zones or near residential neighborhoods.