The Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor is a popular choice in residential, commercial, and light industrial applications due to its efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. It offers improved performance over traditional single-phase motors, especially in scenarios where consistent torque and high starting power are necessary. This article explores the construction, working principles, advantages, and common applications of the Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor.
Introduction to the Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor
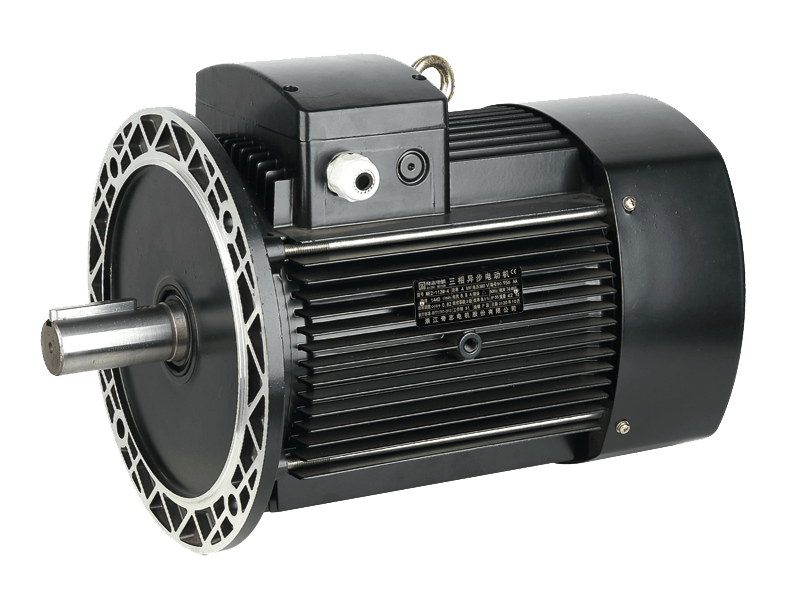
A Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor is a type of single-phase motor that utilizes two capacitors: a start capacitor and a run capacitor. This dual-capacitor arrangement enhances both the starting torque and running efficiency of the motor, making it well-suited for applications requiring high initial torque and stable operation under varying loads.
Construction and Design
The key components of a Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor include:
Stator – The stator has two windings: the main winding and the auxiliary (or start) winding.
Rotor – Typically a squirrel cage rotor, which rotates when the motor is energized.
Start Capacitor – Connected in series with the start winding, it provides the necessary phase shift to start the motor.
Run Capacitor – Connected permanently in the circuit, it ensures smooth and efficient running.
Centrifugal Switch or Relay – This disconnects the start capacitor and start winding once the motor reaches a certain speed.
The dual-capacitor system allows the motor to generate a more balanced magnetic field, improving performance during both startup and continuous operation.
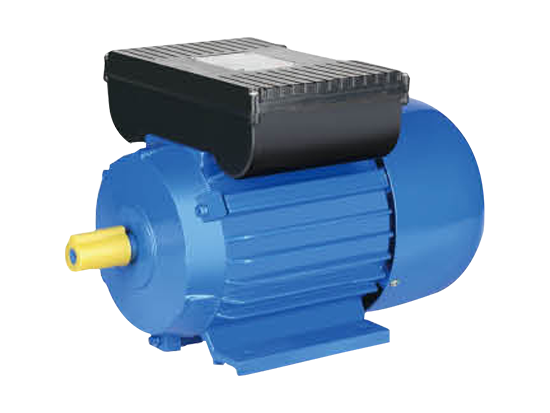

Working Principle
The operation of a Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor begins when voltage is applied to the stator windings. The start capacitor introduces a phase difference between the main and auxiliary windings, generating a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field induces a current in the rotor, causing it to turn.
Once the motor reaches approximately 70–80% of its rated speed, the centrifugal switch opens, disconnecting the start capacitor and auxiliary winding. The run capacitor, which remains in the circuit, continues to provide a phase shift that maintains motor efficiency and torque during normal operation.
Advantages of the Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor
High Starting Torque – Thanks to the start capacitor, the Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor can start heavy loads more effectively.
Improved Efficiency – The run capacitor improves power factor and reduces energy losses during operation.
Smooth Operation – Reduced vibration and noise due to more balanced electromagnetic fields.
Reliability – Fewer moving parts and a simple design lead to increased durability and lower maintenance needs.
Cost-Effectiveness – Offers a good balance between performance and affordability for many applications.
Applications of the Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motor
Due to their versatility and performance, Single-Phase Dual-Capacitor Induction Electric Motors are widely used in various applications, including:
Air Conditioners and Refrigeration Units – These systems require high starting torque to overcome initial resistance in compressors.
Pumps – Especially in water pumps, where steady operation and efficient energy use are critical.
Fans and Blowers – Where quiet and reliable performance is essential.
Washing Machines – Motors must provide enough torque to handle varying load conditions.
Garage Door Openers and Small Machinery – Where dependable starts and continuous operation are necessary.